Class 11 Physics Chapter 3 Notes Motion In A Straight Line
Motion in a Straight Line
A body is said to be in motion if it changes its position with respect to time.
To get more details on Motion in a Straight Line,
Types of Rectilinear/Linear Motion
The Rectilinear Motion or linear motion can be of two types:
- Non-Uniform linear motion with non-zero acceleration or variable velocity
- Uniform linear motion with zero acceleration or constant velocity
The simplest type of one-dimensional motion is Linear motion. As per Newton’s first law of motion, an object will either be in rest or continue to move in a straight line with a uniform velocity unless and until an external force is applied to it.
Linear motion is often mistaken for general motion. Linear motion is a one-dimensional motion but in general, the motion has both magnitude and direction, i.e. an object’s position and velocity are described in vector quantities.
To get more details on Rectilinear Motion,
Uniform Motion in a Straight Line
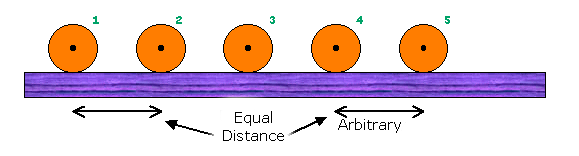
A body is said to be in a uniform motion if it travels in a straight line covering equal distances in equal intervals of time. A body is said to have uniform acceleration if the rate of change of its velocity remains constant.
Example:
If a car travels at a speed of 60 km/hour then it will cover a distance of 1 km/minute. In this sense, the motion of car acceleration is uniform.
For More Information On Motion in One Dimension, Watch The Below Video:
Non-uniform Motion in a Straight Line
A body is said to have a non-uniform motion when the velocity of a body changes by unequal amounts in equal intervals of time. While in movement, the rate of change of its velocity changes at different points of time.
Example:
A boy kicking a football. It might cover 4 meters in the first attempt, 6 meters in the second change, 9 meters in the third attempt and so on as per the velocity exerted by the boy.
To get more details on Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion,
Path Length
The path length is the total length of the path that has to be traversed by the object.
Displacement
Displacement is the change in position of a body. The magnitude of displacement between the same points is proportional to the path length.
To get more details on Displacement Formula,
Uniform Motion
When the displacement of an object is equal in equal time intervals, the motion is said to be uniform, else it is referred to as non-uniform.
Average Speed
Average speed is referred to the ratio between the total path length traversed to the time taken.
To get more details on Average Speed,
Instantaneous Velocity
It is the velocity when the limit of the average velocity has an indefinitely smaller interval of time.
To get more details on Instantaneous Velocity Formula
Average Acceleration
It is the change in velocity corresponding to the time interval with in which the change has accelerated




No comments:
Post a Comment